Work on the Hill
Throughout December, Congress has been engaged in a flurry of major activity as the year draws to a close. A bipartisan agreement is emerging on a year-end health care package, which includes provisions impacting pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs), telehealth expansion, hospital-at-home programs, community health center funding, and health plan transparency. Additionally, the House passed a compromise version of the National Defense Authorization Act (NDAA) on December 11th, which includes significant defense spending and policy changes. To avoid a government shutdown, Congress has reportedly reached a bipartisan deal to extend government funding until March 14th, 2025, including over $100 billion in emergency disaster relief funds.
Lobbyit remains focused on monitoring legislative developments and working with lawmakers to secure NEA’s priorities at the end of the 118th and into the 119th Congress.
Guthrie taps Carter as incoming health subcommittee chair
Rep. Brett Guthrie (R-Ky.), the incoming House Energy and Commerce Chair, announced subcommittee leaders for the next Congress. Rep. Buddy Carter (R-Ga.), a pharmacist, will chair the Health Subcommittee, beating out Reps. Morgan Griffith and Gus Bilirakis. Rep. Diana DeGette (D-Colo.) is expected to be the Democratic counterpart.
Carter, a strong advocate for pharmacy benefit manager reform, plans to extend Covid-era telehealth rules for Medicare patients. With Republicans controlling the White House and Congress, Carter will influence changes to the Inflation Reduction Act’s Medicare drug price negotiations.
Incoming HELP Chair Cassidy to offer new plan to train more doctors
Senator Bill Cassidy, incoming chair of the Senate Health, Education, Labor and Pensions Committee, is leading a bipartisan effort to address the U.S. doctor shortage by adding 5,000 Medicare-funded residency slots from 2027 to 2031. The plan, supported by Senators Catherine Cortez Masto, John Cornyn, and Michael Bennet, prioritizes primary care and psychiatry, and targets rural and underserved areas. It also proposes creating a Graduate Medical Education Policy Council to advise on residency slot distribution. This initiative follows a similar plan by outgoing Finance Committee chair Ron Wyden and aims to mitigate the projected shortage of over 180,000 doctors by 2037, particularly in rural and low-income communities.
CMS Expansions and Medicaid Innovations
Significant regulatory updates shaped the healthcare landscape in October 2024. CMS proposed expanding access to contraceptives and preventive care under the Affordable Care Act, including broader coverage for over-the-counter options without cost-sharing. Skilled nursing facilities face new Medicare revalidation requirements by May 2025, necessitating detailed disclosures on ownership and management. CMS also finalized guidance for the second cycle of Medicare drug price negotiations, expected to lower costs for beneficiaries by 2027.
CMS approved updated essential health benefit benchmark plans for Alaska, Washington, and the District of Columbia, expanding coverage for services like infertility treatments, hearing aids, and nutritional counseling. New Medicare appeals processes were established for patients reclassified from inpatient to outpatient status. Other notable developments include Medicaid approval for traditional Native American health practices in select states and a minimum wage increase for California healthcare workers. These updates reflect ongoing efforts to enhance healthcare access, affordability, and equity while promoting regulatory compliance.
Implications of the 2024 Election on Healthcare Policy: Telehealth, AI, Health Equity, and Life Sciences
The 2024 election results are expected to influence legislative priorities and regulatory oversight in telehealth, health equity, artificial intelligence (AI), and life sciences.
Telehealth remains a bipartisan priority, with extended flexibilities for prescribing certain controlled substances likely to persist. AI policy, heavily influenced by Biden-era regulations, may see a rollback of oversight measures, with a shift toward innovation and reduced government intervention. Health equity initiatives, particularly those tied to DEI programs, are likely to be scaled back, while bipartisan support for rural healthcare may maintain focus on underserved populations.
Life sciences policy is expected to emphasize drug pricing transparency, innovation, and reducing conflicts of interest. The future of FDA user fee programs and expedited Medicare coverage pathways for breakthrough devices remains uncertain, as these policies could undergo significant revisions. The administration’s first 100 days will be pivotal in shaping healthcare priorities, with opportunities and challenges emerging for stakeholders navigating these changes. This evolving landscape underscores the need for vigilance and adaptability as healthcare policy continues to shift.
National health spending spikes to nearly $5T in 2023
In 2023, U.S. health care spending surged by 7.5%, reaching nearly $5 trillion. This increase, the highest since 2020, was driven by more people enrolling in health insurance and seeking medical services. Private health insurance and Medicare were major contributors to this rise. The insured population grew to 92.5%, largely due to increased enrollment in the Obamacare marketplace, supported by enhanced premium subsidies.
Hospital care, prescription drugs, and doctor services saw significant spending increases. Medicaid spending growth slowed, but enrollment remained high at nearly 92 million. Medicare spending also rose, particularly in Medicare Advantage plans.
Despite the spending surge, health care prices grew only 0.6%, indicating that increased service use, not price hikes, drove the spending growth.
House AI Taskforce says Congress should consider enhancing FDA capabilities
A report from the bipartisan House Task Force on Artificial Intelligence suggests that the FDA may need enhanced oversight capabilities to effectively monitor AI in health care. The task force, led by Representatives Jay Obernolte and Ted Lieu, highlights concerns such as privacy risks, biased care delivery, and lack of transparency in AI tools.
The report recommends that Congress consider updating laws to improve the FDA’s post-market evaluation of AI technologies and address liability issues when AI makes mistakes. It also suggests developing voluntary standards for data management and a self-evaluation process for AI developers.
Regulators face challenges in overseeing AI tools due to their variable performance and potential degradation over time. FDA head Robert Califf has indicated a need for more staff to properly vet these tools. Federal regulators have been cautious about new rules to avoid stifling innovation, while health systems seek assurance on safety.
The task force did not address concerns about industry self-policing, particularly involving big tech companies. Both regulators and industry are awaiting President-elect Donald Trump’s stance on AI regulation. Trump has pledged to rescind President Biden’s 2023 executive order on AI and has shown interest in stricter oversight, influenced by Elon Musk’s views on the technology’s potential risks.
Bills by Issue
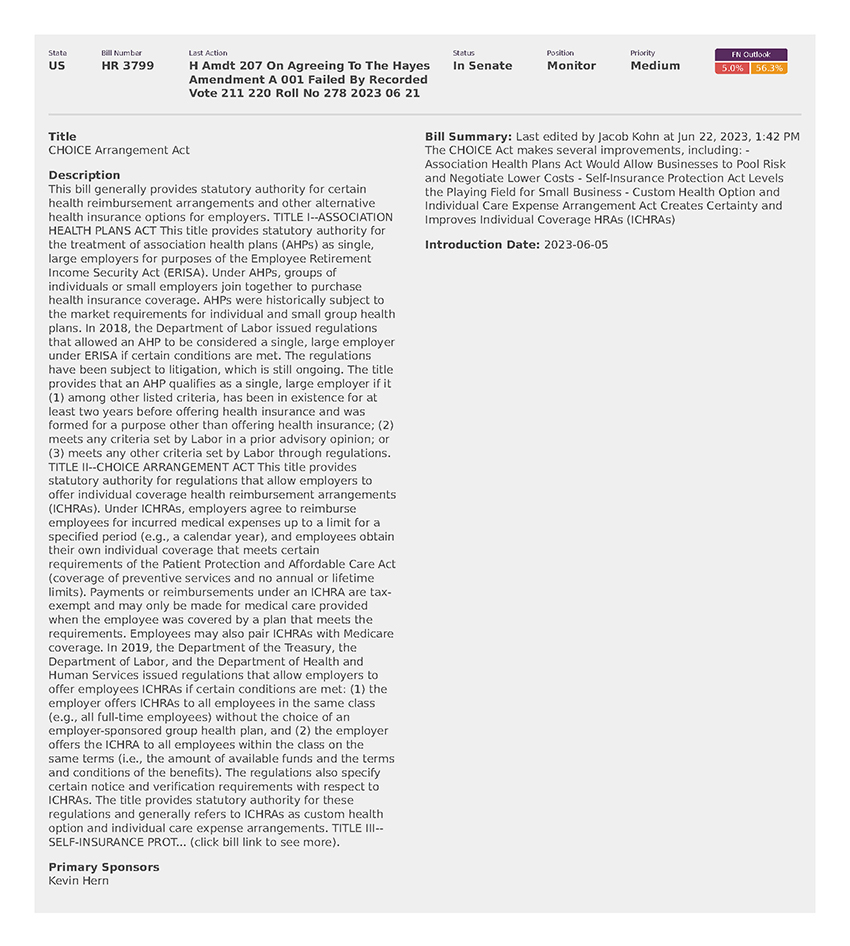
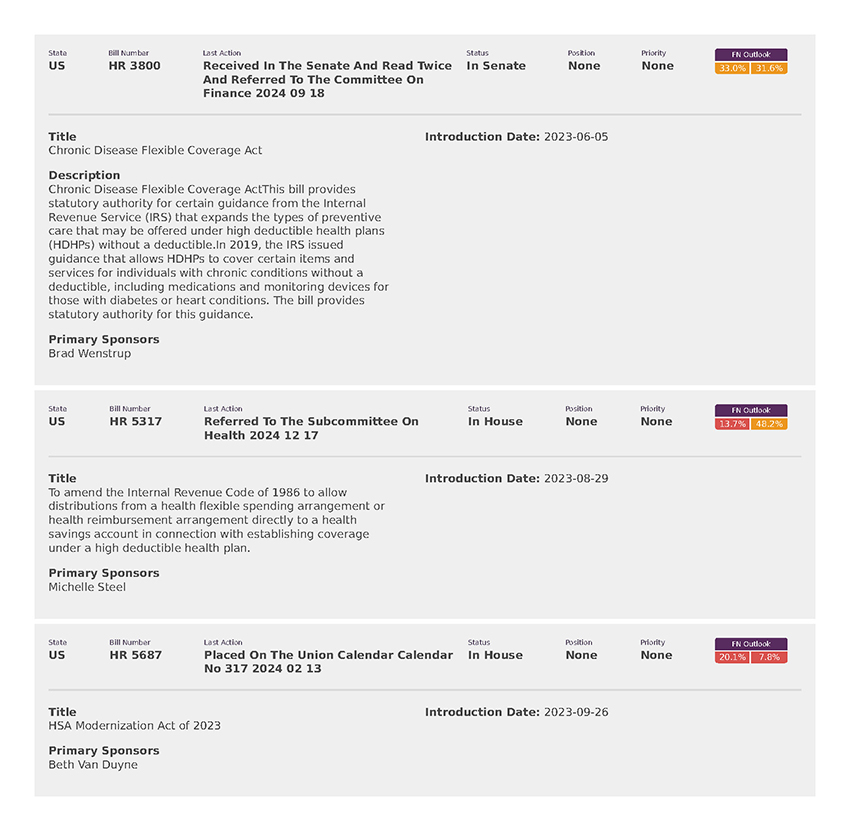
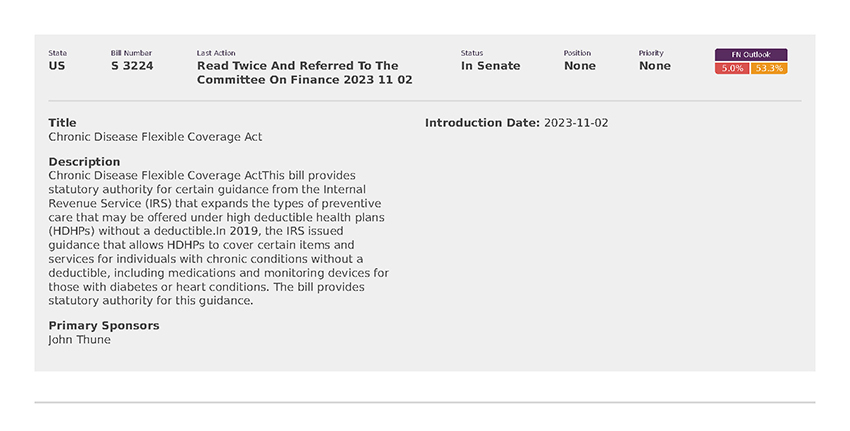
National Employers Association (8)